Search This Blog
An Environmental website whose primary focus is to help everyone understand the impact humans have on the physical environment with resources that help us achieve what we call a safe and clean environment.
Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Carbon Mineralization: A Promising Strategy to Mitigate Climate Change
Carbon mineralization is a natural process that involves the conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) into stable mineral forms through chemical reactions with minerals.
This process occurs naturally over long periods of time, but recently, it has gained attention as a promising strategy to mitigate climate change.
Carbon mineralization has the potential to remove significant amounts of CO2 from the atmosphere and store it for centuries or even millennia.
In this article, we will explore the process of carbon mineralization, its potential benefits and limitations, and its current status as a carbon sequestration strategy.
The Process of Carbon Mineralization
Carbon mineralization occurs when CO2 reacts with minerals containing divalent cations such as magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), and iron (Fe).
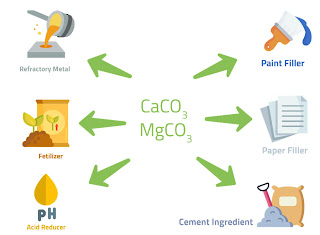
The reaction produces stable carbonates, such as magnesium carbonate (MgCO3), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), and iron carbonate (FeCO3), which are insoluble and stable over long periods of time.
The process occurs naturally in some geological formations, such as oceanic basaltic rocks, but it can also be induced artificially by injecting CO2 into subsurface rocks, where it reacts with minerals to form stable carbonates.Benefits of Carbon Mineralization
Carbon mineralization has several potential benefits as a carbon sequestration strategy. First, it has the potential to sequester large amounts of CO2 over long periods of time.
Estimates suggest that carbon mineralization could potentially sequester billions of tons of CO2 annually, making it a significant contributor to climate change mitigation efforts.
Second, carbon mineralization does not require large land areas or significant changes in land use, unlike other carbon sequestration strategies such as afforestation or soil carbon sequestration.
Third, carbon mineralization does not pose significant risks of leakage or environmental damage, as the stable carbonates are insoluble and do not migrate over long distances.
Limitations of Carbon Mineralization
Despite its potential benefits, carbon mineralization also has some limitations. First, the process requires large amounts of minerals containing divalent cations, which may be limited in some areas.
Second, the process requires significant amounts of energy to produce the necessary conditions for the reaction to occur, such as high temperatures and pressures.
Third, the costs of carbon mineralization are currently high compared to other carbon sequestration strategies, although ongoing research may lead to cost reductions in the future.
Current Status of Carbon Mineralization
Carbon mineralization is currently in the research and development phase, with several pilot projects underway to test the feasibility of the process.
Some of these projects are focused on inducing carbon mineralization in subsurface rocks, while others are exploring the use of mine tailings or other waste materials as a source of minerals for carbon mineralization.
Despite the current challenges and limitations, carbon mineralization has the potential to be a significant contributor to climate change mitigation efforts in the future.
Conclusion
Carbon mineralization is a promising strategy to mitigate climate change by sequestering significant amounts of CO2 over long periods of time.
While the process has some limitations and challenges, ongoing research and development may lead to cost reductions and improved efficiency in the future.
Carbon mineralization should be considered as one of the many tools available to combat climate change, along with other strategies such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable land use practices.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular Posts
Environmentally Persistent Pharmaceutical Pollutants (EPPPs): A Growing Threat to Our Ecosystems
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Circular Economy Important Websites You Should Look At
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments
Post a Comment